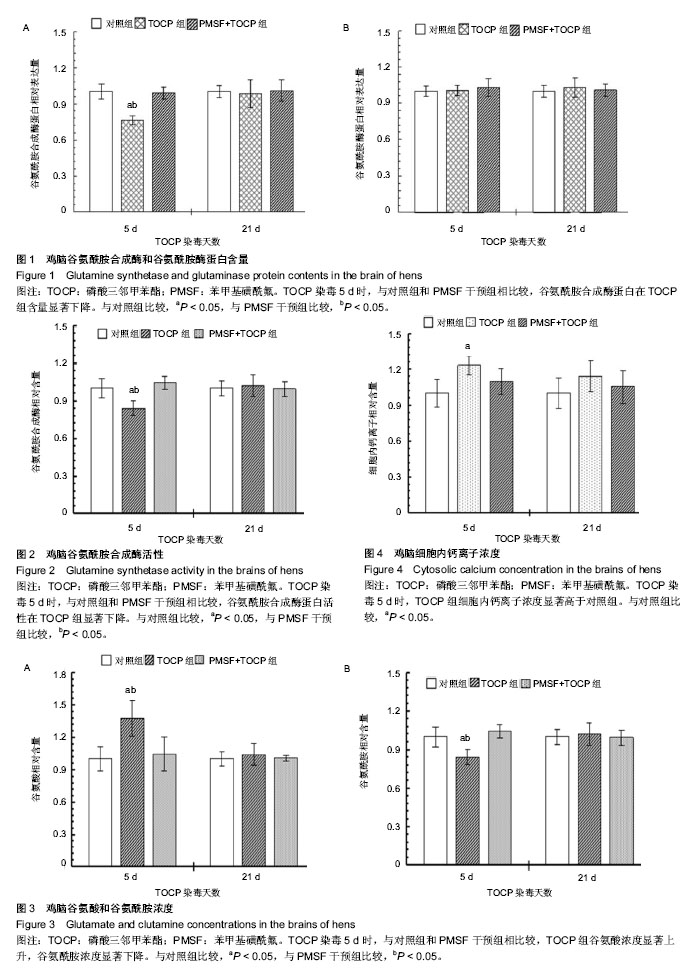
| [1] Abou-donia MB. Organophosphorus ester-induced delayed neurotoxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.1981;21(1): 511-548.
[2] de Ferreyra EC, Villarruel MC, Fernández G, et al.Further studies on the mechanism of the late protective effects of phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver necrosis.Exp Mol Pathol. 1989;50(2):253-269.
[3] Umemura A, Mabe H, Nagai H, et al.Action of phospholipases A2 and C on free fatty acid release during complete ischemia in rat neocortex. Effect of phospholipase C inhibitor and N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist.J Neurosurg. 1992;76(4): 648-651.
[4] el-Fawal HA, Ehrich MF. Calpain activity in organophosphorus- induced delayed neuropathy (OPIDN): effects of a phenylalkylamine calcium channel blocker. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;28(679):325-329.
[5] Choudhary S, Gill KD. Protective effect of nimodipine on dichlorvos-induced delayed neurotoxicity in rat brain(1). Biochem Pharmacol.2001;62(9): 1265-1272.
[6] Masoud A,Kiran R,Sandhir R.Modulation of dopaminergic system and neurobehavioral functions in delayed neuropathy induced by organophosphates. Toxicol Mech Methods.2011; 21(1): 1-5.
[7] Qian Y, Venkatraj J, Barhoumi R, et al. Comparative non-cholinergic neurotoxic effects of paraoxon and diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP) on human neuroblastoma and astrocytoma cell lines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2007; 219 (2-3): 162-171.
[8] Emerick GL, Ehrich M, Jortner BS, et al. Biochemical, histopathological and clinical evaluation of delayed effects caused by methamidophos isoforms and TOCP in hens: ameliorative effects using control of calcium homeostasis. Toxicology. 2012;302(1): 88-95.
[9] Emerick GL,Peccinini RG,de Oliveira GH. Organophosphorus-induced delayed neuropathy: a simple and efficient therapeutic strategy. Toxicol Lett.2010; 192(2): 238-244.
[10] Piao FY, Yamauchi T, Ma N. The effect of Calcicol as calcium tonic on delayed neurotoxicity induced by organophosphorus compounds. Toxicol Lett.2003;143(1): 65-71.
[11] Abou-donia MB. The cytoskeleton as a target for organophosphorus ester-induced delayed neurotoxicity (OPIDN). Chem Biol Interact.1993;87(1-3): 383-393.
[12] Abou-donia MB. Involvement of cytoskeletal proteins in the mechanisms of organophosphorus ester-induced delayed neurotoxicity. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1995;22(5): 358-359.
[13] Walton HS, Dodd PR. Glutamate-glutamine cycling in Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Int.2007;50(7-8): 1052-1066.
[14] Stirling DP, Stys PK. Mechanisms of axonal injury: internodal nanocomplexes and calcium deregulation. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16(4): 160-170.
[15] Hertz L, Dringen R, Schousboe A, et al. Astrocytes: glutamate producers for neurons. J Neurosci Res. 1999; 57(4): 417-428.
[16] Bröer S, Brookes N. Transfer of glutamine between astrocytes and neurons. J Neurochem.2001;77(3): 705-719.
[17] Xu B,Xu ZF,Deng Y,et al.Protective effects of MK-801 on methylmercury-induced neuronal injury in rat cerebral cortex: involvement of oxidative stress and glutamate metabolism dysfunction. Toxicology.2012;300(3): 112-120.
[18] Lajdoba I, Spustaba V, Oksa A, et al. Intracellular calcium homeostasis in patients with early stages of chronic kidney disease: effects of vitamin D3 supplementation. Nephrol Dial Transplant.2009;24(11): 3376-3381.
[19] Jokanovic M, Kosanovic M, Brkic D, et al. Organophosphate induced delayed polyneuropathy in man: an overview. Clin Neurol Neurosurg.2011;113(1): 7-10.
[20] Choi DW. Calcium and excitotoxic neuronal injury. Ann N Y Acad Sci.1994;15(747):162-171.
[21] Crish SD, Calkins DJ.Neurodegeneration in glaucoma: progression and calcium-dependent intracellular mechanisms. Neuroscience.2011;10(176):1-11.
[22] Zou J, Wang YX, Dou FF, et al. Glutamine synthetase down-regulation reduces astrocyte protection against glutamate excitotoxicity to neurons. Neurochem Int. 2010; 56(4): 577-584.
[23] Vardimon L. Neuroprotection by glutamine synthetase. Isr Med Assoc J.2000;2 Suppl:46-51.
[24] Liu W, Xu Z, Deng Y, et al. Excitotoxicity and oxidative damages induced by methylmercury in rat cerebral cortex and the protective effects of tea polyphenols. Environ Toxicol.2012; 29(3):269-283.
[25] Yu X, He GR, Sun L, et al. Assessment of the treatment effect of baicalein on a model of Parkinsonian tremor and elucidation of the mechanism. Life Sci.2012;91(1-2): 5-13.
[26] Castegna A, Palmieri L,Spera I,et al.Oxidative stress and reduced glutamine synthetase activity in the absence of inflammation in the cortex of mice with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neuroscience.2011;30(185): 97-105.
[27] Ben-Dror I, Havazelet N, Vardimon L.Developmental control of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity in embryonic retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(3): 1117-1121.
[28] Pu HF, Young AP.Glucocorticoid-inducible expression of a glutamine synthetase-CAT-encoding fusion plasmid after transfection of intact chicken retinal explant cultures. Gene. 1990;89(2): 259-263.
[29] Berko-Flint Y, Levkowitz G, Vardimon L. Involvement of c-Jun in the control of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity during development of chicken retinal tissue. EMBO J.1994; 13(3): 646-654.
[30] Oren A, Herschkovitz A, Ben-Dror I,et al.The cytoskeletal network controls c-Jun expression and glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity in an antagonistic and cell-type-specific manner. Mol Cell Biol.1999;19(3): 1742-1750.
[31] Piao F, Ma N, Yamamoto H, et al. Effects of prednisolone and complex of vitamin B1, B2, B6 and B12 on organophosphorus compound-induced delayed neurotoxicity. J Occup Health. 2004;46(5): 359-364.
[32] Baker T,Stanec A.Methylprednisolone treatment of an organophosphorus-induced delayed neuropathy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.1985;79(2): 348-352.
[33] Damodaran TV, Rahman AA, Abou-Donia MB.Early differential induction of C-jun in the central nervous system of hens treated with diisopropylphosphorofluoridate (DFP). Neurochem Res.2000;25(12): 1579-1586. |